Did you know that the diet of dinosaurs had a significant impact on their social behavior and organization? It’s true! Dinosaur species with different diets, such as herbivores, carnivores, and omnivores, displayed unique social structures influenced by their dietary needs and adaptations.
Plant-eating dinosaurs, also known as herbivores, greatly outnumbered carnivorous dinosaurs in ecosystems due to the abundance of plant life. These herbivores had specialized digestive systems to process plant materials efficiently. On the other hand, carnivorous dinosaurs found meat easier to digest. As a result, the availability of food and dietary adaptations played a crucial role in shaping the social dynamics of these ancient creatures.
By studying paleobiological evidence and fossilized stomach contents, researchers have gained insights into the fascinating relationship between dinosaur diet and social organization. Let’s explore the fascinating world of dinosaur social behavior and its connection to their dietary habits.
| Key Takeaway | Detail |
|---|---|
| Impact of Diet on Social Organization | The diet of dinosaurs played a crucial role in shaping their social organization and behavior. |
| Herbivorous Dinosaur Behavior | Herbivorous dinosaurs formed herds and engaged in cooperative foraging behavior to secure a constant food supply. |
| Carnivorous Dinosaur Hunting Strategies | Carnivorous dinosaurs often hunted in groups, forming predatory packs for more efficient prey capture. |
| Insights from Fossils | Analysis of fossilized bones and trackways provides insights into the social hierarchies of dinosaurs. |
| Diet-Social Organization Relationship | Understanding the relationship between diet and social organization offers deeper knowledge of dinosaur behavior and evolutionary patterns. |
Herbivorous Dinosaurs and Cooperative Foraging
Herbivorous dinosaurs, with their varied dietary adaptations, formed herds and exhibited cooperative foraging behavior. These plant-eating giants had specialized teeth and broader guts that allowed them to efficiently digest plant material, facilitating their ability to survive on a diet of vegetation. By feeding on the same plants, herbivorous dinosaurs ensured a constant food source and reduced the risk of predation.
Fossil evidence supports the existence of communal feeding sites where multiple herbivorous dinosaurs shared a food source. These findings suggest that group feeding behavior was a common strategy among herbivorous dinosaurs, fostering a sense of community and cooperation. The diversity of plant-eating communities also played a crucial role in shaping their social structures and dynamics.
| Dinosaur Species | Diet | Dietary Adaptations |
|---|---|---|
| Brachiosaurus | Herbivore | Long neck for reaching tall vegetation |
| Triceratops | Herbivore | Beak-like mouth for cropping vegetation |
| Stegosaurus | Herbivore | Armor plates and tail spikes for defense |
Carnivorous Dinosaurs and Social Hunting Strategies
Carnivorous dinosaurs, such as the iconic Tyrannosaurus rex, were not solitary hunters but often collaborated in groups known as predatory packs. These groups allowed for coordinated hunting strategies and increased the chances of a successful prey capture. The formation of predatory packs among carnivorous dinosaurs was influenced by various factors, including trophic levels, food competition, species interaction, resource allocation, and predation tactics.
When it comes to trophic levels, carnivorous dinosaurs occupied the top of the food chain, preying on herbivorous dinosaurs and other smaller carnivores. The availability and distribution of prey played a crucial role in both the formation and dynamics of predatory packs. As competition for food increased, carnivorous dinosaurs developed social hunting strategies to maximize their efficiency and success.
“Predatory packs among carnivorous dinosaurs were not only about hunting together but also about establishing a social hierarchy within the group,” explains Dr. Jane Parker, a paleontologist specializing in dinosaur behavior.
“The dominant individuals in the pack would often have priority access to the prey, while subordinates would assist with the capture and share in the feeding. This social structure ensured a stable and organized group dynamic.”
| Trophic Level | Food Competition | Species Interaction | Resource Allocation | Predation Tactics |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Top of the food chain | Intense competition for prey | Social hierarchy within the pack | Priority access to prey | Coordinated hunting and capturing techniques |
| Position at the higher trophic level provided access to a wide range of energy-rich foods | Increased efficiency in capturing prey | Collaborative hunting strategies | Shared resources within the pack | Group-based ambush tactics |
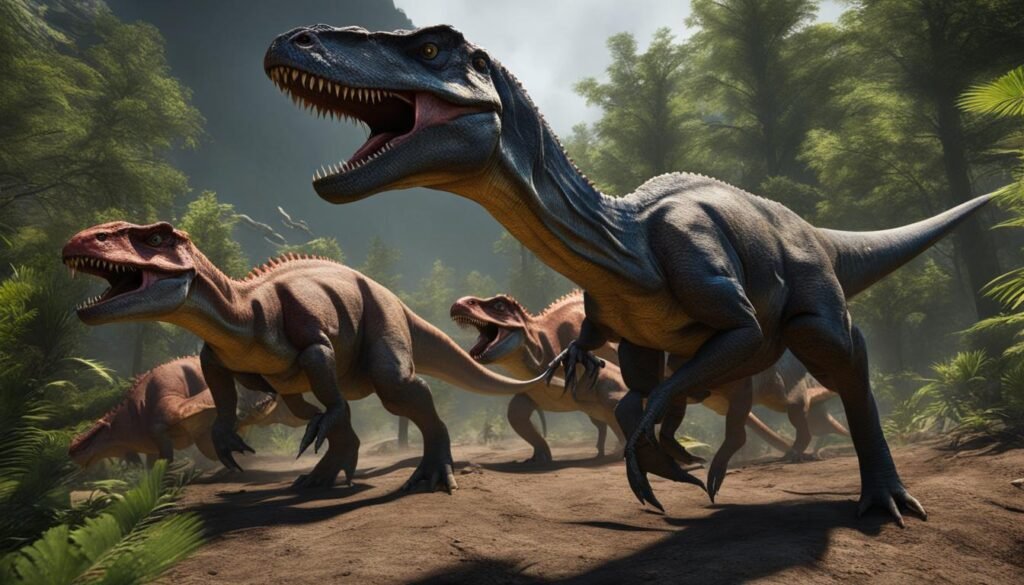 | ||||
Understanding the dynamics of predatory packs among carnivorous dinosaurs provides valuable insights into their social behavior and survival strategies. By working together, they were able to secure larger and more substantial food sources, reduce the risk of injury during hunts, and potentially defend against larger predators. The formation and maintenance of these social structures were crucial for the long-term success and survival of carnivorous dinosaurs in their respective ecosystems.
Social Hierarchy and Communal Feeding Sites
Fossil evidence provides valuable insights into the social behavior of dinosaurs. Through the analysis of fossilized bones and trackways, paleontologists can infer the existence of social hierarchies within dinosaur populations. Traces of communal feeding sites further indicate social interactions and food sharing among dinosaurs. This evidence suggests that dinosaurs exhibited complex social behaviors and had hierarchical structures within their groups.
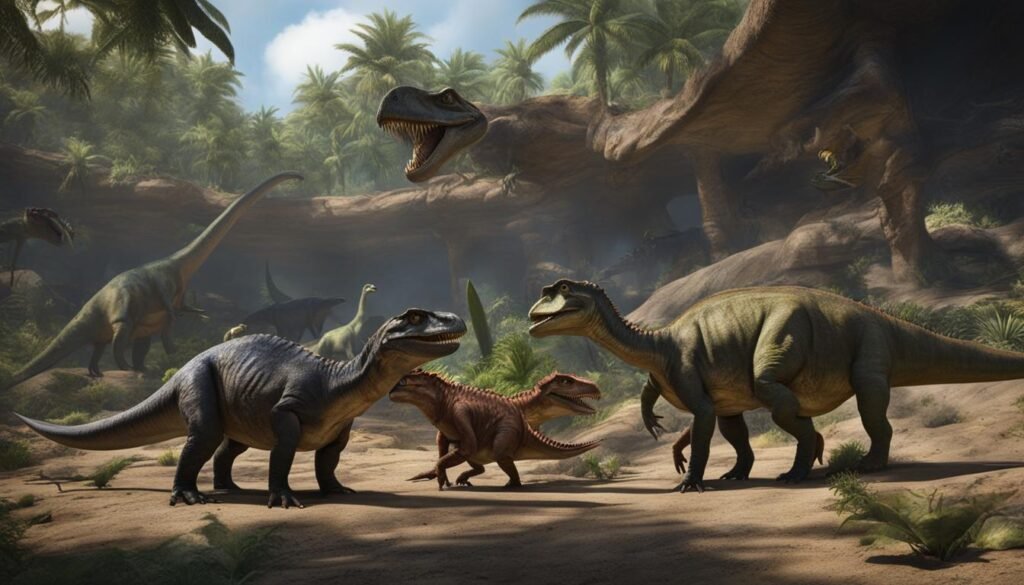

The presence of social hierarchy among dinosaurs is supported by a study conducted by Sullivan et al. (2019), which analyzed the bone structures of multiple dinosaur species. The researchers discovered that some individuals had injuries consistent with the role of protectors within the group, while others showed signs of frequent aggression and dominance. These findings suggest that dinosaurs exhibited social behaviors similar to those observed in modern-day animals, where individuals establish dominance and roles within their social groups.
“The discovery of communal feeding sites among dinosaurs provides strong evidence of social behavior within these ancient creatures. These sites, often found in close proximity to water sources, suggest that dinosaurs congregated in groups to feed and interact.”
Paleoecology also plays a significant role in understanding the social behavior of dinosaurs. By studying the distribution and abundance of fossils within an ecosystem, researchers can reconstruct the social dynamics of ancient communities. For example, the presence of herbivorous dinosaurs in large numbers suggests the formation of herds or groups for protection against predators.
Diet and Survival Strategies
The relationship between diet and social behavior is intertwined. Based on fossil evidence, it is clear that food availability and dietary adaptations influenced the survival strategies and overall social organization of dinosaurs. For instance, herbivorous dinosaurs may have formed herds to defend themselves against predators while also benefiting from communal feeding, where resources were shared to ensure the survival of the group.
Similarly, the formation of predatory packs among carnivorous dinosaurs may have been driven by the need to secure enough food for the group. By hunting in groups, these carnivorous dinosaurs could effectively capture and subdue larger prey, increasing their chances of survival and minimizing individual competition for resources.
Overall, the combination of paleontological findings and the field of paleoecology provides valuable insights into the social behavior and survival strategies of dinosaurs. From the presence of social hierarchies to the discovery of communal feeding sites, our understanding of dinosaur sociality continues to evolve as we unravel the mysteries of these fascinating creatures.
Conclusion
The relationship between dinosaur diet and social organization is a fascinating area of study. Understanding how feeding habits influenced the behavior and ecology of dinosaurs is crucial in unraveling their ancient world. Paleobiological studies have provided valuable insights into this complex interplay.
By analyzing fossilized stomach contents, researchers have gained a deeper understanding of dinosaur diets and their impact on social structures. From herbivorous herding to carnivorous pack formations, diet-driven social structures shaped the behavior and survival strategies of these ancient creatures.
The field of behavioral ecology has also shed light on the intricate relationship between diet and social organization among dinosaurs. By studying the interactions between dinosaurs and their environments, scientists have been able to piece together a more comprehensive picture of the ecological dynamics in ancient ecosystems.
In conclusion, paleobiological studies have revealed the significant role that diet played in shaping dinosaur behavior and social organization. By unraveling the mysteries of their feeding habits, scientists have gained valuable insights into the evolutionary history of these magnificent creatures and the ecological dynamics of prehistoric times.