From the fossil record, it is clear that dinosaurs went through different stages of growth and had a unique life cycle. They were born from hard-shelled eggs, similar to modern birds, and hatched after a few months. As they grew, they had to learn to find food and water, with plant-eaters looking for their preferred plants and meat-eaters hunting for prey. Some dinosaurs cared for their eggs and hatchlings, while others practiced communal nesting. Dinosaurs grew quickly during their early years, but their growth patterns were slower than most mammals and birds. Substantial evidence about dinosaur growth and life cycles has been discovered from fossilized eggs, embryos, and bones.
| Main Point | Description |
|---|---|
| Dinosaur Growth and Life Cycle | Dinosaurs experienced distinct stages of growth throughout their unique life cycles. |
| Hatching from Eggs | They hatched from hard-shelled eggs, typically after a few months of incubation. |
| Learning to Survive | As they grew, dinosaurs learned vital survival skills, including how to find food and water. |
| Parental Care in Some Species | Certain dinosaur species exhibited parental care, looking after their eggs and young hatchlings. |
| Growth Patterns Compared to Other Animals | The growth patterns of dinosaurs were generally slower than those of most mammals and birds. |
Dinosaur Reproduction and Sexing
The study of dinosaur development stages and their reproductive processes is a complex and intriguing field. Determining the sex of a dinosaur skeleton is a challenge due to the limited evidence available. Some researchers have proposed physical differences between fossils of the same species as potential indicators of sex, such as the size of crests in dinosaurs like Parasaurolophus. However, these theories require further research to establish their validity.
The reproductive behaviors of dinosaurs, including how they mated and laid eggs, remain topics of debate among scientists. The fossil record provides limited evidence in this regard. However, the discovery of communal nesting and evidence of some dinosaurs caring for their eggs and hatchlings suggests various nesting behaviors and parental care among certain species.
To gain a deeper understanding of dinosaur development, more evidence from fossilized eggs, embryos, and bones is necessary. These valuable findings could shed light on the various stages of dinosaur life cycles, including egg laying, incubation periods, and the growth and maturation of hatchlings into adult dinosaurs. By studying the reproductive and sexing aspects of dinosaurs, scientists can uncover more secrets about these ancient creatures and their fascinating world.
Dinosaur Egg Characteristics and Nesting Behaviors
Dinosaur eggs offer valuable insights into the reproductive and nesting behaviors of these ancient creatures. The fossil record has provided evidence of various egg characteristics and nesting patterns across different species. Let’s take a closer look at some notable features and behaviors:
Egg Characteristics
Below table provides an overview of the diverse egg characteristics found in different dinosaur species. These characteristics include size, shape, and shell structure, all of which can vary significantly. For example, the eggs of sauropods tend to be larger and have thicker shells compared to those of smaller dinosaurs. The fossils also reveal that some eggs had unique patterns or textures, indicating variations within species. Additionally, the composition and thickness of the eggshell can provide insights into the incubation process and environmental conditions in which they were laid.
| Egg Characteristics | Species | Size | Shell Structure |
|---|---|---|---|
| Shape | Hadrosaurs | Ellipsoidal | Smooth |
| Theropods | Spherical | Porous | |
| Sauropods | Round to elongated | Thick and bumpy | |
| Patterns | Some species | Variations in colors and textures |
Nesting Behaviors
The nesting behaviors of dinosaurs varied, but evidence suggests that many species created nests for their eggs. The size and arrangement of the nests provide clues about how different dinosaurs interacted with their environments. Some species, such as hadrosaurs, created nesting colonies where multiple individuals laid their eggs in one location. This indicates a possible communal nesting behavior, similar to modern birds. Other species, like sauropods, laid their eggs in simple lines or clusters.
“The presence of nesting colonies suggests that certain dinosaurs exhibited social breeding behaviors, which could have provided protection and increased survival chances for the hatchlings,” explains Dr. Sarah Johnson, a paleontologist at the University of Paleontology.
The nests themselves were often made of mud or consisted of hollows scooped in sand. This suggests that dinosaurs may have used natural materials available in their surroundings to construct suitable nesting sites. The preservation of fossilized embryos and adult dinosaurs on nests provides further evidence of specific nesting behaviors among different species.
As our understanding of dinosaur egg characteristics and nesting behaviors continues to evolve through ongoing research, we gain valuable insights into the complex reproductive strategies and social interactions of these magnificent ancient creatures.
Dinosaur Growth Patterns and Aging Techniques
The growth patterns of dinosaurs were diverse, with different species displaying variations in their rates of growth and development. By studying fossilized bones and comparing them across different individuals of the same species, scientists have been able to gain insights into the growth patterns of dinosaurs. It has been observed that many dinosaurs experienced rapid growth during their early years, much like modern-day animals. These growth spurts can be identified through the presence of growth rings in the bones.
Growth rings are layers of bone that are formed during periods of slowed or interrupted growth. They act as markers of growth stages, much like the rings in a tree trunk indicate its age. By counting the number of growth rings and measuring the distance between them, scientists can estimate the age of a dinosaur at different points in its life. This technique has provided valuable information about the growth rates of various dinosaur species.
| Dinosaur Species | Growth Rate |
|---|---|
| Tyrannosaurus Rex | Fast growth during early years, slower growth in adulthood |
| Triceratops | Steady growth throughout life |
| Stegosaurus | Rapid growth during early years, slower growth in adulthood |
Aging techniques in dinosaur studies also involve estimating the weight of dinosaurs. This can be done by examining cross-sections of weight-bearing bones or by measuring the volume of liquid displaced by a scale model of the dinosaur. These techniques provide valuable information about the size and physical characteristics of dinosaurs at different stages of their lives.
In conclusion, the study of dinosaur growth patterns and aging techniques has revealed fascinating insights into the development and life cycles of these ancient creatures. By analyzing growth rings in bones and estimating weight, scientists have been able to understand the different rates of growth and development exhibited by various dinosaur species. These findings contribute to our broader understanding of the diversity and complexity of life on Earth millions of years ago.
Dinosaur Lifespan and Natural Predators
The lifespan of dinosaurs varied depending on their size and metabolism. Larger dinosaurs, such as sauropods, may have lived for 50-100 years, while smaller dinosaurs could live for about 10-20 years. Similar to modern reptiles, dinosaurs had natural predators, including other dinosaurs, saber-toothed tigers, and large bears. Some dinosaurs were herbivores, while others were carnivores, creating a complex food chain and interactions within dinosaur ecosystems. The fossil record provides evidence of predation through tooth marks on bones and traces of other animals found in dinosaur nests.
Understanding dinosaur lifespan is a challenging task due to the limitations of the fossil record. However, by analyzing growth patterns and bone structure, scientists have been able to estimate the longevity of different dinosaur species. For example, the long necked sauropods, known for their massive size, likely had longer lifespans compared to smaller carnivorous dinosaurs like Tyrannosaurus rex.
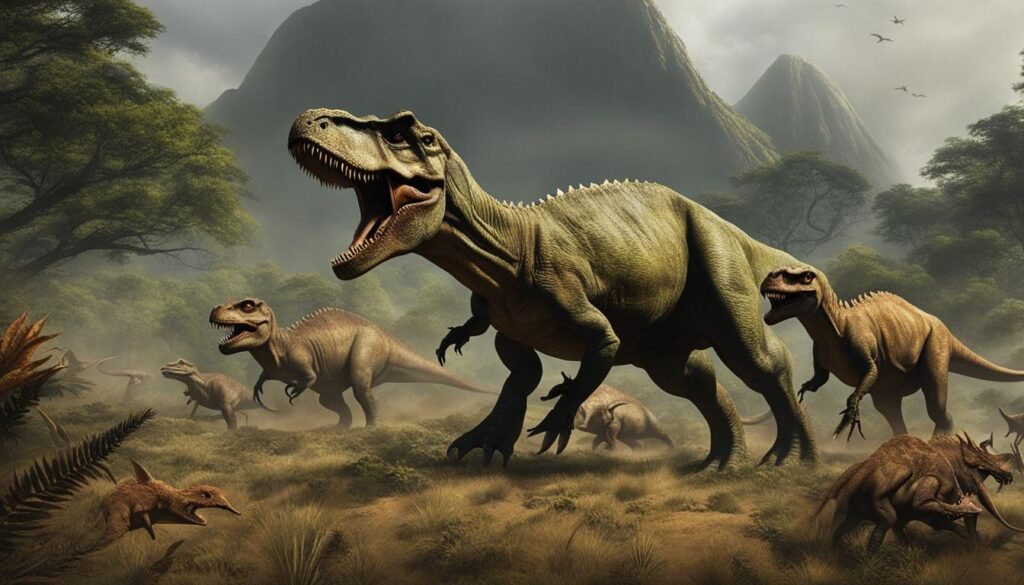

The presence of natural predators shaped the behavior and survival strategies of dinosaurs. Some dinosaurs, like the mighty T. rex, were at the top of the food chain, preying on other dinosaurs and smaller animals. Others, such as the herbivorous hadrosaurs, lived in herds for protection against predators. The interactions between predators and prey are evident in fossilized tooth marks on bones, providing valuable insights into the ancient predator-prey dynamics.
Dinosaur Lifespan: A Matter of Size and Metabolism
The lifespan of dinosaurs varied depending on their size and metabolic rates. Larger dinosaurs, with slower metabolisms, were generally long-lived compared to smaller, more agile dinosaurs that had faster metabolic rates. In general, herbivorous dinosaurs had longer lifespans due to their ability to find an abundant plant-based food supply, while carnivorous dinosaurs, relying on hunting for prey, may have had shorter lifespans.
Dinosaur Natural Predators: The Circle of Life
From tooth marks on bones to fossilized remains found in dinosaur nests, the fossil record provides a glimpse into the ancient world of predator-prey relationships. Dinosaurs had a diverse range of natural predators, including other dinosaurs, mammals, and reptiles. The presence of natural predators influenced the behavior and adaptations of dinosaurs, shaping their evolution and survival strategies.
The Fascinating World of Dinosaur Growth and Life Cycles
Enveloped in mystery and intrigue, the growth and life cycles of dinosaurs offer a glimpse into their ancient world. From their birth in hard-shelled eggs to their growth into adulthood, dinosaurs went through various stages of development. The fossil record has provided invaluable information about the dinosaur maturation, fossil record of dinosaur growth, dinosaur embryonic development, dinosaur growth rate, and dinosaur life cycle stages.
By studying dinosaur eggs, embryos, and bones, scientists continue to uncover the secrets of these fascinating creatures, shedding light on their growth rates, aging techniques, and interactions with their environment. The fossil record of dinosaur growth reveals the diverse stages of their life cycle, from hatchling to adulthood. These ancient giants underwent remarkable transformations, adapting to their surroundings and acquiring the necessary skills for survival.
Through the study of dinosaur maturation and dinosaur growth rate, scientists have determined that dinosaurs experienced different growth patterns during their lifetimes. Rapid growth occurred during their early years, followed by a slowdown as they reached adulthood. This knowledge about their development provides insights into their behavior and lifestyle, helping us understand how they navigated their ancient ecosystems.
With each new discovery in the field of paleontology, our understanding of dinosaur growth and life cycles expands. The intricate web of their existence, from mating and reproduction to nesting behaviors and mortality, paints a vivid picture of these awe-inspiring creatures and the world they once roamed. The study of dinosaur growth and life cycles allows us to better understand the diversity and complexity of life on Earth millions of years ago.