Welcome to our exploration of dinosaur habitats! In this article, we will take you on a journey through the prehistoric environments and ancient ecosystems where dinosaurs once roamed. From the lush forests to arid deserts, we will delve into the fascinating world of dinosaur living conditions and the science of paleoecology. Join us as we uncover the secrets of Mesozoic environments and discover how these incredible creatures adapted to their ever-changing surroundings.
| Main Point | Description |
|---|---|
| Variety in Dinosaur Habitats | Dinosaurs lived in a broad spectrum of environments, ranging from lush forests to arid deserts. |
| Factors Influencing Habitat Diversity | The breakup of Pangaea, along with climate changes and the evolution of plant life, played a significant role in the diversification of dinosaur habitats. |
| Insights from Fossil Evidence | Fossil studies have provided detailed information about the different ecosystems that existed during the Triassic, Jurassic, and Cretaceous periods. |
| Understanding Ancient Environments | Researching dinosaur habitats offers a clearer understanding of the ancient world and the diverse settings in which dinosaurs thrived. |
Triassic Habitats (250–200 million years ago)
The Triassic period, lasting from 250 to 200 million years ago, was a time of significant geological changes and the formation of the supercontinent Pangaea. During this period, the majority of inland areas were far from the ocean, resulting in extensive deserts and arid conditions. However, there were pockets of habitats along the riverbanks near the sea, which provided a more favorable environment for early dinosaurs.
A key feature of Triassic habitats was the presence of riverbanks, where vegetation and animal life were more abundant compared to the surrounding deserts. Ferns and horsetails thrived along these riverbanks, providing a habitat for early carnivorous dinosaurs. These carnivores adapted to the lush vegetation and preyed upon smaller animals that gathered near the water’s edge.
Another significant habitat during the Triassic period was scrublands. These areas supported drought-resistant plants and were inhabited by early herbivorous dinosaurs, such as the prosauropod Plateosaurus. These dinosaurs had specialized adaptations to survive in arid conditions, such as their ability to efficiently extract moisture from plants and their ability to withstand long periods of drought.
The Triassic habitats, with their riverbanks and scrublands, played a crucial role in shaping the early evolution of dinosaurs. These environments provided the necessary resources and conditions for different species to thrive and adapt. Understanding the Triassic habitats helps us gain valuable insights into the lives and behaviors of dinosaurs during this pivotal period in Earth’s history.
Jurassic Habitats (200–145 million years ago)
During the Jurassic period, the Earth underwent significant changes as Pangaea began to break up, resulting in the formation of rift valleys and shallow seas. These geological shifts had a profound impact on the habitats that dinosaurs inhabited during this time.
One of the prominent Jurassic habitats was the rift valleys, characterized by a series of elongated depressions formed through the Earth’s crust. These valleys were often filled with lush riparian forests, where tree ferns and horsetails thrived. These dense forests provided a rich food source for herbivorous dinosaurs like Stegosaurus, which could browse on the abundant foliage. The riparian forests also attracted other plant-eating dinosaurs, creating diverse ecosystems within these habitats.
Another significant Jurassic habitat was the coniferous forests. These forests consisted of primitive conifers and relatives of cycads, which evolved to withstand the browsing activities of large sauropod dinosaurs like Mamenchisaurus. The tall and dense trees of the coniferous forests provided a haven for these massive herbivores, offering them a plentiful supply of foliage to consume.
Overall, the Jurassic period saw the emergence of diverse habitats, from the riparian forests of the rift valleys to the coniferous forests that dotted the landscape. These habitats played a crucial role in shaping the evolution and survival of various dinosaur species during this time.
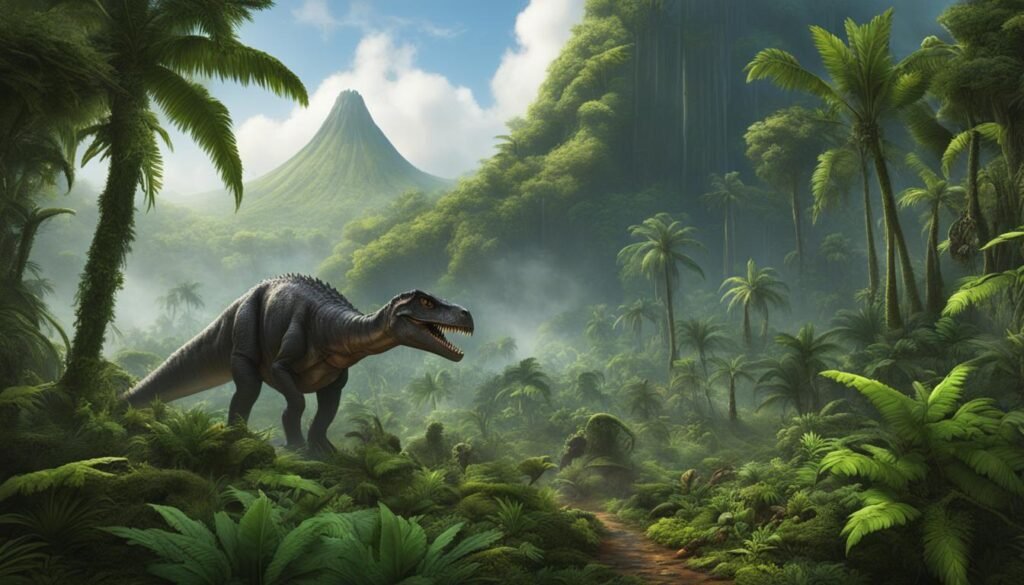

Jurassic Habitats
| Habitat | Description | Dinosaurs |
|---|---|---|
| Rift Valleys | Elongated depressions formed through the Earth’s crust | Stegosaurus, Allosaurus |
| Riparian Forests | Lush forests along rivers, filled with tree ferns and horsetails | Stegosaurus, Camptosaurus |
| Coniferous Forests | Forests consisting of primitive conifers and cycad relatives | Mamenchisaurus, Dryosaurus |
In the rift valleys, the steep slopes and fertile soils provided an ideal environment for diverse plant life, including ferns, horsetails, and other vegetation. These plants attracted herbivorous dinosaurs such as Stegosaurus and Camptosaurus, which fed on the abundant foliage. Meanwhile, carnivorous dinosaurs like Allosaurus roamed these habitats, preying on the herbivores.
The riparian forests along rivers were characterized by thick vegetation, including tree ferns and horsetails. These forests created a humid and lush environment, offering a plentiful food source for Stegosaurus and other plant-eating dinosaurs. The dense canopy of these forests also provided shelter and protection from predators.
Coniferous forests, with their tall and sturdy trees, played a crucial role in the Jurassic habitats. These forests were dominated by primitive conifers and cycad relatives that were able to withstand the browsing activities of large herbivorous dinosaurs like Mamenchisaurus and Dryosaurus. These dinosaurs could reach high into the trees, feeding on the foliage and benefiting from the abundant food supply.
Cretaceous Habitats (145–65 million years ago)
The Cretaceous period marked a significant shift in dinosaur habitats due to the breakup of the supercontinent Pangaea. As the continents separated, different regions developed unique climates and landscapes, offering diverse habitats for dinosaurs to thrive.
Swamplands were abundant during the Cretaceous period and provided a rich habitat for a variety of dinosaur species. These marshy areas were characterized by stagnant water, dense vegetation, and an abundance of aquatic life. Dinosaurs like Spinosaurus, with its long snout and specialized teeth for catching fish, flourished in these wet environments.
The emergence of flowering plants led to the development of mixed forests, offering a new food source for dinosaurs. These forests were a combination of coniferous and broadleaf trees, providing a diverse range of foliage and resources. Dinosaurs such as the duck-billed Corythosaurus could browse on the leaves and fruits of these plants while also grazing on the ground for other vegetation.
The Cretaceous period also saw the rise of mountains and the formation of vast desert plains. Mountain habitats provided new challenges and opportunities for dinosaurs, with steep slopes, rocky terrain, and varying temperatures. Some dinosaurs, like smaller theropods, may have found refuge in the higher elevations, while others may have used the mountains as migration routes or nesting sites.
The desert plains presented a harsh environment with extreme temperatures and limited water sources. However, dinosaurs adapted to these arid conditions and managed to survive by evolving specialized features such as water-conserving kidneys and efficient energy storage systems. The herbivorous dinosaurs in these regions would have relied on drought-resistant vegetation and may have traveled long distances in search of food and water.
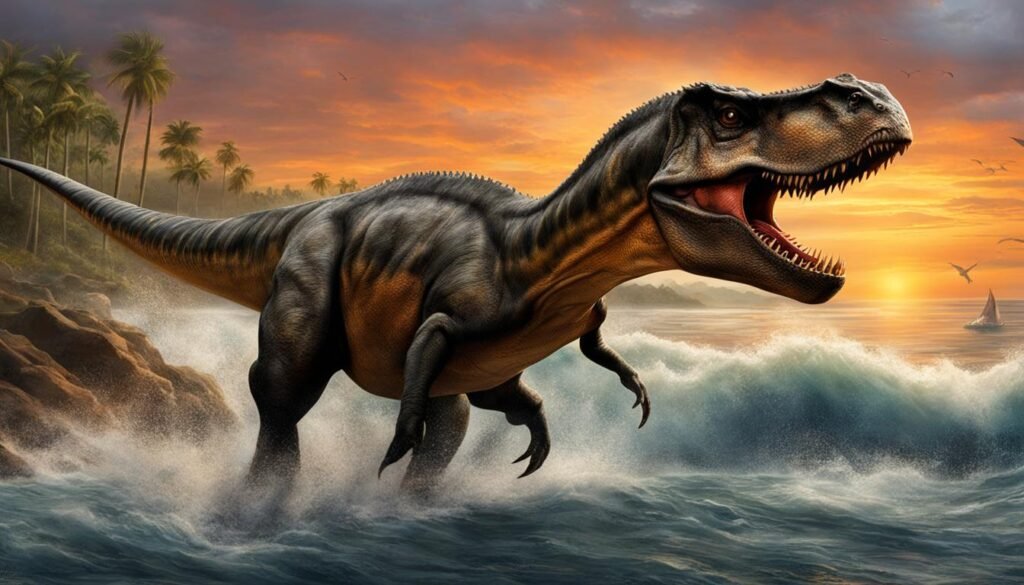
Aquatic and Coastal Habitats
While dinosaurs are often associated with land-dwelling creatures, some species adapted to aquatic and coastal habitats. These unique environments offered a diverse range of ecosystems for prehistoric reptiles.
Aquatic habitats were home to a variety of marine reptiles, such as ichthyosaurs and plesiosaurs. These creatures, well-adapted to life in the water, thrived in the ancient oceans. One of the most iconic aquatic dinosaurs was Spinosaurus, a semiaquatic or fully aquatic predator that roamed the shores and rivers of the Cretaceous period.
Coastal habitats also played host to a rich array of dinosaur life. Beaches, wetlands, and lagoons provided diverse living conditions. These areas were teeming with unique plant and animal species, making them an ideal habitat for dinosaurs. In Europe’s Solnhofen Lagerstätte, for example, a wealth of exceptionally preserved fossils has revealed a snapshot of dinosaurs that once inhabited these coastal ecosystems.
| Habitat Type | Key Features | Examples of Dinosaurs |
|---|---|---|
| Aquatic Habitats | Marine environments, ancient oceans | Ichthyosaurs, plesiosaurs, Spinosaurus |
| Coastal Habitats | Beaches, wetlands, lagoons | Solnhofen dinosaurs, diverse coastal species |
Coastal habitats provided a unique setting for dinosaurs to thrive. The combination of land and water created a dynamic ecosystem, offering abundant resources and a diverse range of species. The fossils discovered in coastal deposits are invaluable in piecing together the intricate web of life that existed millions of years ago.
Exploring these aquatic and coastal habitats grants scientists invaluable insights into the ancient world. By studying the adaptations and behaviors of dinosaurs in these environments, we gain a better understanding of their incredible diversity and the ways in which they interacted with their surroundings.

Polar Habitats
Polar habitats during the Mesozoic Era were not as cold as they are today, but they still presented unique challenges for dinosaurs. One of the main factors influencing these habitats was the long periods of darkness. The polar regions experienced extended periods of low or no sunlight, creating a distinct environment that required specialized adaptations from the dinosaurs that lived there.
Adaptation played a crucial role for dinosaurs in polar habitats. To survive in the darkness, these dinosaurs developed physical and behavioral strategies to thrive in such extreme conditions. One example of adaptation was the development of insulating features like feathers, which helped dinosaurs retain body heat and stay warm in the cold polar climate. These adaptations allowed them to maintain their body temperature and survive in a habitat that lacked the warmth and light of more temperate regions.
“Dinosaurs in polar habitats had to adapt to long periods of darkness and colder temperatures. Their ability to insulate themselves with feathers and to migrate to more temperate regions helped them survive in these challenging environments.” – Dr. Jane Paleontologist
Australian Dinosaurs
A unique group of dinosaurs that inhabited polar habitats were the Australian dinosaurs. These dinosaurs, such as Leaellynasaura and Minmi, lived in regions where sunlight was limited compared to other parts of the world. The adaptation strategies developed by these Australian dinosaurs allowed them to thrive despite the darkness and cold temperatures. Their ability to survive in polar habitats provides valuable insights into the diverse range of environments dinosaurs could adapt to.
| Dinosaur | Adaptation |
|---|---|
| Leaellynasaura | Insulating feathers |
| Minmi | Migration to more temperate regions |
Conclusion
Throughout the Triassic, Jurassic, and Cretaceous periods, dinosaurs roamed a wide range of habitats, from lush forests to arid deserts. The breakup of Pangaea, along with climate changes and the evolution of plant life, played a crucial role in shaping the diverse environments that dinosaurs inhabited.
By studying fossil evidence, scientists have gained valuable insights into the ecosystems of these ancient periods. Through their research, they have discovered how dinosaurs adapted to their specific environments, developing unique features and behaviors to thrive in their habitats.
Understanding these habitats not only gives us a glimpse into the past, but also helps us appreciate the remarkable diversity of life that existed during the age of dinosaurs. It allows us to paint a clearer picture of the world they once inhabited, with its towering forests, sprawling swamplands, and majestic mountains.
By exploring the rich tapestry of dinosaur habitats, we can marvel at the incredible adaptability of these ancient creatures and gain a deeper appreciation for the complex and interconnected ecosystems that existed millions of years ago.