Welcome to our exploration of dinosaur feeding strategies and social dynamics. In this article, we will delve into the fascinating world of these ancient creatures, uncovering their adaptations for survival. Through the study of paleobiology and fossil evidence, we can gain valuable insights into the feeding behaviors and social interactions among dinosaur species.
| Key Takeaway | Detail |
|---|---|
| Feeding Strategies and Survival | Dinosaur feeding strategies are key to understanding their survival adaptations in different environments. |
| Insights from Paleobiology | Paleobiology and fossil evidence shed light on the diverse feeding behaviors and social dynamics of dinosaurs. |
| Social Interactions | Cooperative hunting methods and competition for resources played significant roles in shaping dinosaur social interactions. |
| Ecological and Evolutionary Success | Studying dinosaurs’ feeding behavior provides insights into their ecological impact and evolutionary success. |
| Fossilized Teeth as Clues | Fossilized teeth are crucial in revealing information about the diets and foraging behaviors of different dinosaur species. |
The Importance of Dinosaur Feeding Behavior
Dinosaur feeding behavior played a crucial role in their ecological and evolutionary success. Understanding how these ancient creatures obtained their food provides valuable insights into their paleobiology and survival strategies. By studying their feeding behavior, researchers can gain a deeper understanding of the energy requirements, reproductive strategies, habitat preferences, and population ecology of dinosaurs.
Feeding behavior directly influenced the energy requirements of dinosaurs. Herbivorous dinosaurs, such as the Triceratops, needed to consume large amounts of vegetation to meet their nutritional needs. In contrast, carnivorous dinosaurs, like the Velociraptor, required a diet rich in meat to sustain their energy levels. By analyzing their feeding behavior, scientists can estimate the amount and type of food that different dinosaur species needed to survive.
The reproductive strategies of dinosaurs were also closely linked to their feeding behavior. The availability of food resources played a significant role in determining when and where dinosaurs would mate and lay their eggs. Some dinosaur species, like the Maiasaura, congregated in large nesting colonies near abundant food sources, ensuring the survival of their offspring. Others, such as the Tyrannosaurus rex, were solitary predators that needed to actively hunt for food to sustain themselves and their young.
Energy Requirements of Herbivorous and Carnivorous Dinosaurs
| Dinosaur Species | Feeding Behavior | Energy Requirements |
|---|---|---|
| Triceratops | Herbivorous | High |
| Velociraptor | Carnivorous | High |
| Maiasaura | Herbivorous | Medium |
| Tyrannosaurus rex | Carnivorous | High |
Studying dinosaur feeding behavior allows researchers to reconstruct the paleobiology of these ancient creatures and gain a better understanding of their ecological roles. By examining the fossilized teeth of dinosaurs, scientists can infer the types of food they consumed and their dietary adaptations. For example, sharp, serrated teeth suggest a carnivorous diet, while flat, grinding teeth indicate herbivorous feeding habits. This knowledge helps researchers determine the ecological impact of different dinosaur species and their contributions to ancient ecosystems.
In conclusion, dinosaur feeding behavior provides valuable insights into their paleobiology, energy requirements, reproductive strategies, and ecological roles. By studying how these ancient creatures obtained their food, researchers can piece together the puzzle of their survival and understand the complex dynamics of prehistoric ecosystems. The study of dinosaur feeding behavior continues to uncover fascinating discoveries and expands our knowledge of the evolutionary history of life on Earth.
Insights from Feeding Habits: Roles in the Food Chain
Dinosaurs, both carnivorous and herbivorous, played pivotal roles in the prehistoric food chain, contributing to the intricate dynamics of predator-prey interactions and ecological niches. Their feeding habits and interactions shaped the structure and function of ancient ecosystems, influencing the distribution and abundance of species within trophic levels.
In the prehistoric food chain, carnivorous dinosaurs acted as top predators, exerting control over lower trophic levels. Their feeding habits were characterized by hunting and consuming other dinosaurs, establishing a dynamic predator-prey relationship. The large size and powerful jaws of carnivorous dinosaurs, such as the Tyrannosaurus rex, allowed them to overpower their prey and maintain their position at the top of the food chain.
On the other hand, herbivorous dinosaurs occupied lower trophic levels and played a crucial role as primary consumers. They were responsible for consuming vegetation, such as ferns, cycads, and conifers. Their feeding habits influenced the availability of resources within the ecosystem, shaping the composition and structure of plant communities. By browsing on plants, herbivorous dinosaurs indirectly affected the distribution and abundance of other organisms in their environment.
| Role in the Food Chain | Feeding Habits |
|---|---|
| Carnivorous Dinosaurs | Hunting and consuming other dinosaurs |
| Herbivorous Dinosaurs | Consuming vegetation such as ferns, cycads, and conifers |
“The intricate web of interactions within the prehistoric food chain highlights the interconnectedness and interdependence of species in ancient ecosystems. Understanding the feeding habits of dinosaurs allows us to reconstruct the complexities of these long-lost environments and gain insights into the ecological niches they occupied.” – Dr. Elizabeth Grant, Paleontologist
The feeding habits of dinosaurs also influenced the development and maintenance of ecological niches. Different species of dinosaurs specialized in consuming specific types of food, occupying distinct ecological roles. This niche differentiation minimized competition for resources, allowing for the coexistence of diverse dinosaur species in the same ecosystem. Through their feeding habits, dinosaurs shaped the structure and function of ancient ecosystems, contributing to the overall biodiversity and ecological stability of the prehistoric world.
The Significance of Feeding Habits in Prehistoric Ecosystems
By studying the feeding habits of dinosaurs, paleontologists can unravel the intricate dynamics of ancient ecosystems. Understanding the roles of dinosaurs in the food chain, their feeding interactions, and their impact on ecological niches provides valuable insights into the paleobiology and survival strategies of these magnificent creatures. Through the analysis of fossilized teeth, bone structures, and other paleontological evidence, scientists can piece together the puzzle of dinosaur feeding behavior and gain a deeper understanding of the prehistoric world.
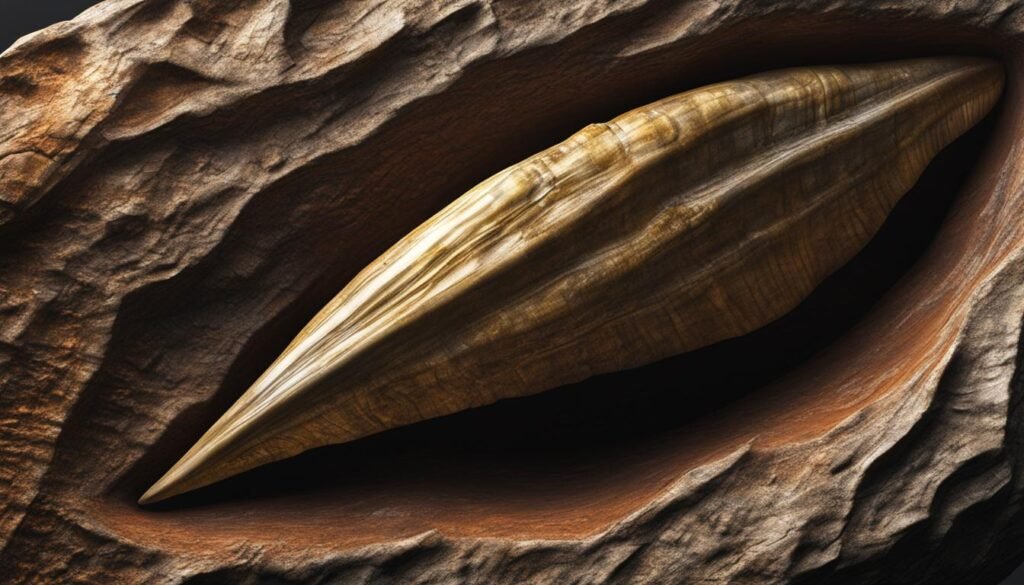
Fossilized Teeth as Clues: Uncovering Dinosaur Diets
One of the key ways researchers gain insights into the diets of dinosaurs is through the examination of fossilized teeth. These ancient teeth offer valuable clues about the types of food dinosaurs consumed and their foraging behavior. By analyzing the shape, size, and wear patterns of these teeth, scientists can paint a picture of the dietary adaptations that allowed dinosaurs to survive and thrive in their respective ecosystems.
Fossilized teeth provide evidence of the incredible diversity in dinosaur diets. Some teeth indicate a carnivorous diet, with sharp, serrated edges designed for tearing flesh. These teeth were likely used by predatory dinosaurs such as T. rex to capture and consume other animals. On the other hand, herbivorous dinosaurs had teeth adapted for chewing and grinding plant matter. These teeth were often flat and shaped like broad, ridged surfaces, allowing for efficient processing of tough plant material.
By studying the fossilized teeth of different dinosaur species, scientists can also gain insights into their foraging behavior. For example, teeth with varying degrees of wear can provide information about the types of food dinosaurs preferred and how they interacted with their environment. Additionally, the presence of dental adaptations, such as specialized teeth for cracking or crushing hard objects, can reveal specific dietary habits and strategies employed by dinosaurs.
Dietary adaptations witnessed in dinosaur teeth:
- Sharp, serrated teeth for tearing flesh
- Flat, ridged teeth for grinding plant matter
- Teeth with varying degrees of wear indicate different food preferences
- Dental adaptations for cracking or crushing hard objects
In conclusion, fossilized teeth provide valuable insight into the diets and foraging behavior of dinosaurs. By examining the characteristics of these teeth, scientists can infer the types of food dinosaurs consumed and how they adapted to their ecological niche. This information helps us better understand the ancient ecosystems in which dinosaurs lived and sheds light on the incredible diversity and survival strategies of these fascinating creatures.

Ahistorical and Historical Approaches to Studying Dinosaur Feeding Behavior
When it comes to studying dinosaur feeding behavior, researchers employ a combination of ahistorical and historical approaches. Ahistorical approaches focus on analyzing the physical characteristics of fossils, such as skeletal structures and teeth, to infer feeding behavior. This involves examining the shape, size, and wear patterns of teeth, as well as the presence of specialized structures that may indicate specific dietary adaptations.
On the other hand, historical approaches leverage the concept of form-function correlations and phylogenetic position to infer function through homology. By comparing the anatomical features and evolutionary relationships of different dinosaur species, researchers can make inferences about their feeding strategies based on similarities with modern-day animals.
Both ahistorical and historical approaches have their advantages and limitations. Ahistorical approaches provide direct evidence from the fossils themselves, offering valuable insights into the actual physical characteristics of extinct organisms. However, they rely on assumptions about the functional significance of these characteristics, which can be challenging to verify without direct observation.
“Ahistorical approaches focus on analyzing the physical characteristics of fossils, while historical approaches leverage evolutionary relationships to infer function through homology.”
Historical approaches, on the other hand, provide a broader context by considering the evolutionary history of dinosaurs and their relationships with other organisms. This allows for comparative analysis and the identification of shared characteristics that may be indicative of similar feeding behaviors. However, historical approaches are based on assumptions about the evolutionary relationships and functional similarities between organisms, which may not always be accurate.
In conclusion, the study of dinosaur feeding behavior combines both ahistorical and historical approaches to gain a comprehensive understanding of how these ancient creatures interacted with their environment. By analyzing the physical characteristics of fossils and considering their evolutionary relationships, researchers can infer valuable insights into the feeding strategies and adaptations of dinosaurs. However, it is important to approach these inferences with caution and continually refine our understanding as new evidence emerges.

Conclusion
The study of dinosaur feeding strategies and social dynamics provides valuable insights into their survival strategies. These ancient creatures employed various tactics such as group hunting, territorial foraging, and dietary diversity to adapt and thrive in their environments.
Group hunting was a common survival strategy for carnivorous dinosaurs. By cooperating in hunting, they could take down larger prey and reduce the risk of injury. This collaborative effort allowed them to secure sufficient food resources for survival.
Territorial foraging was another important survival strategy observed among herbivorous dinosaurs. They established and defended territories to ensure access to abundant food sources. By controlling specific areas, they could minimize competition and maximize their chances of survival.
Dietary diversity was crucial for the long-term survival of dinosaurs. By having a wide range of food options, they could adapt to changing environmental conditions and avoid over-reliance on a single food source. This dietary flexibility played a significant role in their ability to persist over millions of years.