Tyrannosaurus Rex, or T. rex for short, was one of the most fearsome predators that ever lived. It was the king of the dinosaurs, ruling over the land with its massive jaws and powerful legs. Tyrannosaurus Rex was also one of the last dinosaurs to exist before a mass extinction wiped them out 66 million years ago.

Basic Information
| Feature | Details |
|---|---|
| Time Period | Late Cretaceous |
| Diet | Carnivore |
| Length | Up to 12.4 m (41 ft) |
| Weight | Up to 10 tonnes (11 tons) |
| Size | Gigantic |
| Posture | Bipedal |
| Locations | USA, Canada, Mexico |
| Continent | North America |
| Type | Theropods |
| Habitats | Forest, Grasslands, Floodplains |
Description of Tyrannosaurus Rex
Historical Context
The first fossils of Tyrannosaurus rex were discovered by paleontologist Barnum Brown in Montana in 1902. He later found a more complete skeleton in 1908, which he sent to the American Museum of Natural History in New York. The museum’s president, Henry Fairfield Osborn, named the new species Tyrannosaurus rex in 1905, and mounted the skeleton for public display in 1915. Since then, more than 50 specimens of T. rex have been found, making it one of the best-known dinosaurs. Some of the most famous specimens include Sue, the largest and most complete T. rex ever found, Stan, a very well-preserved and articulated skeleton, and Scotty, the heaviest and oldest T. rex known.
Physical Attributes
Tyrannosaurus rex was a massive and powerful animal, with a large and robust skull that housed a brain twice as big as that of other large carnivorous dinosaurs. It had a keen sense of smell, hearing, and vision, which helped it locate and track its prey. It had about 60 teeth that were serrated and curved backwards, ideal for slicing through flesh and bone. Its jaws could exert a bite force of up to 57,000 newtons (12,800 pounds), the strongest of any terrestrial animal ever measured. Its neck was thick and muscular, allowing it to support its heavy head and resist the struggles of its prey.
Tyrannosaurus rex had a long and muscular tail that balanced its body and helped it maneuver while running or turning. Its hind limbs were strong and sturdy, with three-toed feet that ended in sharp claws. It could walk at a speed of about 5 km/h (3 mph), but some estimates suggest that it could run up to 25 km/h (15 mph) or even faster. However, running at such high speeds would have been risky and costly for such a large animal, so it may have preferred to ambush or chase down slower or weaker prey.
Tyrannosaurus rex had very short forelimbs that were proportionally smaller than those of any other large carnivorous dinosaur. Each arm had only two digits that bore claws. The function of these arms is still debated, but they may have been used for grasping or holding prey, mating, or balance.
Tyrannosaurus rex had a scaly skin that was mostly gray or brown in color, with some possible variations such as stripes or spots. Some specimens show evidence of injuries or diseases, such as broken bones, infections, tumors, or bite marks from other T. rexes or other predators.
Feeding Habits
Tyrannosaurus rex was an apex predator that fed on large herbivorous dinosaurs such as Triceratops, Edmontosaurus, Ankylosaurus, and Hadrosaurus. It may have also scavenged on carcasses left by other predators or natural causes. It used its powerful jaws and teeth to tear off chunks of flesh and bone from its prey, swallowing them whole or spitting out unwanted parts. It could consume up to 230 kg (500 lbs) of meat in one bite, and up to 20% of its body weight in one meal. It had a fast metabolism and a high growth rate, requiring a lot of food to sustain itself.
Tyrannosaurus rex may have hunted alone or in pairs, using its senses and intelligence to locate and ambush its prey. It may have also cooperated or competed with other T. rexes for food or territory. Some fossils show evidence of cannibalism among T. rexes, either as a result of predation or scavenging.
Unique Features
Tyrannosaurus rex had several features that made it unique among dinosaurs and other animals. One of them was its large and complex brain, which gave it a high degree of intelligence and cognitive abilities. It had a well-developed sense of smell, which was enhanced by a large olfactory bulb in its brain. It also had a good sense of hearing, which was aided by a long cochlea in its inner ear. It had binocular vision, which allowed it to perceive depth and distance. It may have also had color vision, which could help it distinguish prey from the environment.
Another unique feature of Tyrannosaurus rex was its vocalization. It had a large and complex larynx, which enabled it to produce a variety of sounds. Some studies suggest that it could roar at frequencies as low as 9 Hz, which would be inaudible to humans but could travel long distances and cause vibrations in the ground. It may have also used infrasound, which is sound below the human hearing range, to communicate with other T. rexes or intimidate its prey.
Movement and Speed
Tyrannosaurus rex was a bipedal animal that walked on its hind legs and used its tail for balance. It had a horizontal posture, with its body parallel to the ground and its head slightly raised. It had a flexible spine that allowed it to bend and twist its body while moving or turning.
Tyrannosaurus rex was capable of moving at different speeds, depending on the situation and the terrain. It could walk at a leisurely pace of about 5 km/h (3 mph), but it could also sprint at speeds of up to 25 km/h (15 mph) or even faster, according to some estimates. However, running at such high speeds would have been risky and costly for such a large animal, so it may have preferred to ambush or chase down slower or weaker prey.
Tyrannosaurus rex had a high center of mass and a narrow base of support, which made it prone to falling or tipping over if it lost its balance or encountered an obstacle. It also had a large turning radius, which made it difficult to change direction quickly or sharply. Therefore, it had to be careful and skillful when moving at high speeds or on uneven terrain.
Cultural Impact
Tyrannosaurus rex is one of the most popular and influential dinosaurs in modern culture. It has been featured in many books, movies, TV shows, video games, toys, and other media, often as the main antagonist or the symbol of power and ferocity. Some of the most famous examples include Jurassic Park, King Kong, The Land Before Time, Toy Story, and Godzilla.
Tyrannosaurus rex has also inspired many artists, scientists, and enthusiasts to study and recreate its appearance, behavior, and ecology. It has been the subject of many scientific debates and discoveries, such as its growth rate, bite force, feathered ancestors, social life, and vocalization. It has also been the source of many myths and misconceptions, such as its inability to see stationary objects, its rivalry with Triceratops, or its status as the largest land predator ever.
Tyrannosaurus rex is widely regarded as the king of the dinosaurs and the ultimate representation of prehistoric life. It is admired for its strength, intelligence, and charisma, but also feared for its aggression, violence, and dominance. It is a symbol of both awe and terror, both fascination and dread.
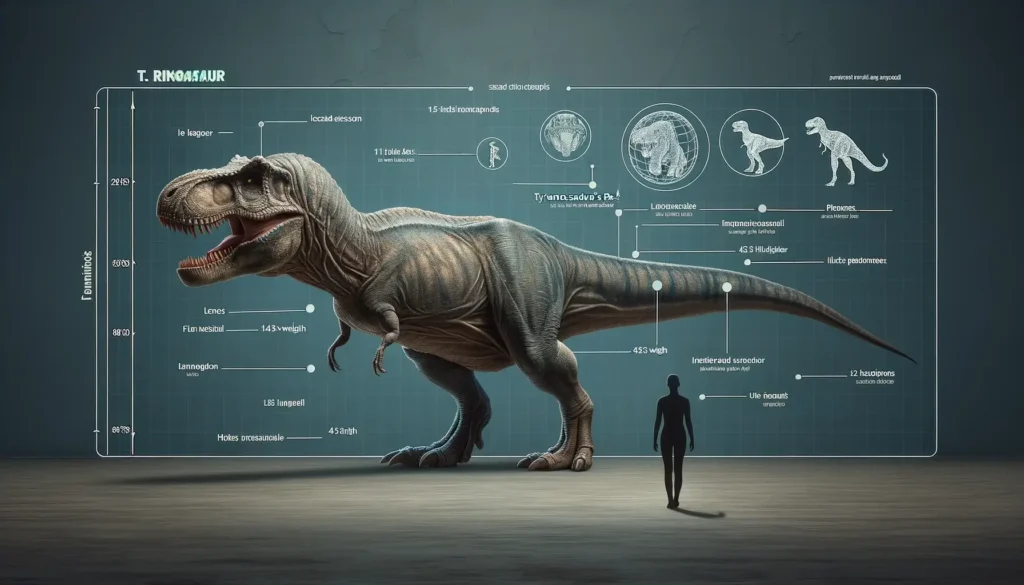

Interesting Facts
- Tyrannosaurus had the largest brain of any known dinosaur, relative to its body size. It had a brain volume of about 530 cubic centimeters (32 cubic inches), comparable to that of a modern chimpanzee. It also had a large olfactory bulb that gave it a keen sense of smell.
- Tyrannosaurus may have been able to produce sounds similar to birds or crocodiles. Some scientists have suggested that it could roar, hiss, growl, or even coo. These sounds may have been used for communication, intimidation, or courtship.
- Tyrannosaurus may have lived in social groups or families. Some fossil sites have shown evidence of multiple individuals of different ages and sizes living together. These groups may have cooperated in hunting, defending, or caring for their young.
Related Dinosaurs
- Albertosaurus: A smaller cousin of Tyrannosaurus that lived in Canada. It had longer arms and a more slender build than T. rex.
- Tarbosaurus: A close relative of Tyrannosaurus that lived in Asia. It was similar in size and appearance to T. rex, but had smaller teeth and a narrower skull.
- Lythronax: An early ancestor of Tyrannosaurus that lived in North America. It had a short snout and a wide mouth that gave it a fierce look.







