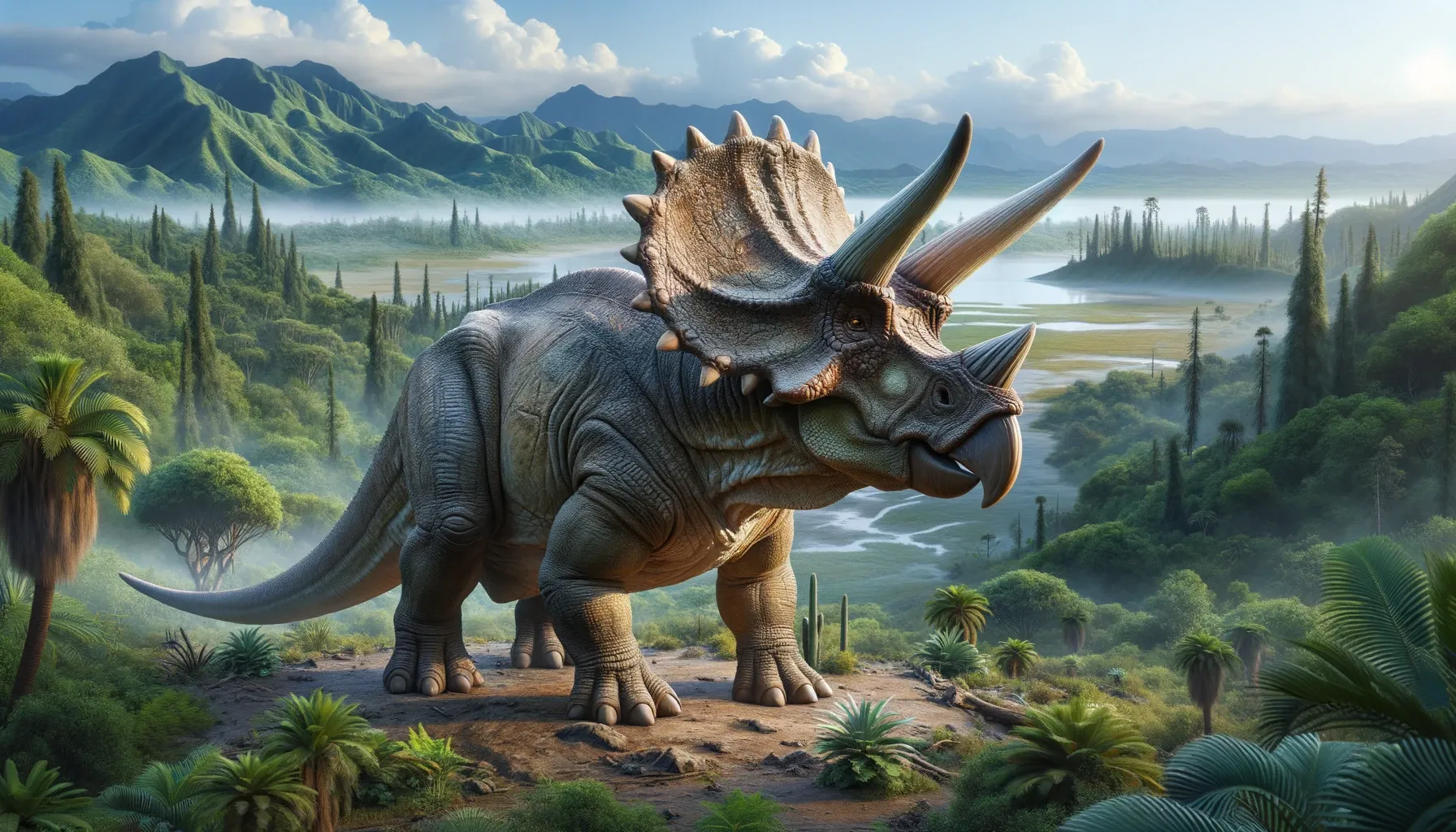
Triceratops was a herbivorous dinosaur that lived in the Late Cretaceous period, about 68 to 66 million years ago. It is famous for its three horns and its large frill, which it used for defense and display. Triceratops was one of the largest and most common members of the ceratopsian family, which included other horned and frilled dinosaurs.

Basic Information
| Feature | Details |
|---|---|
| Time Period | Late Cretaceous (68-66 million years ago) |
| Diet | Herbivore |
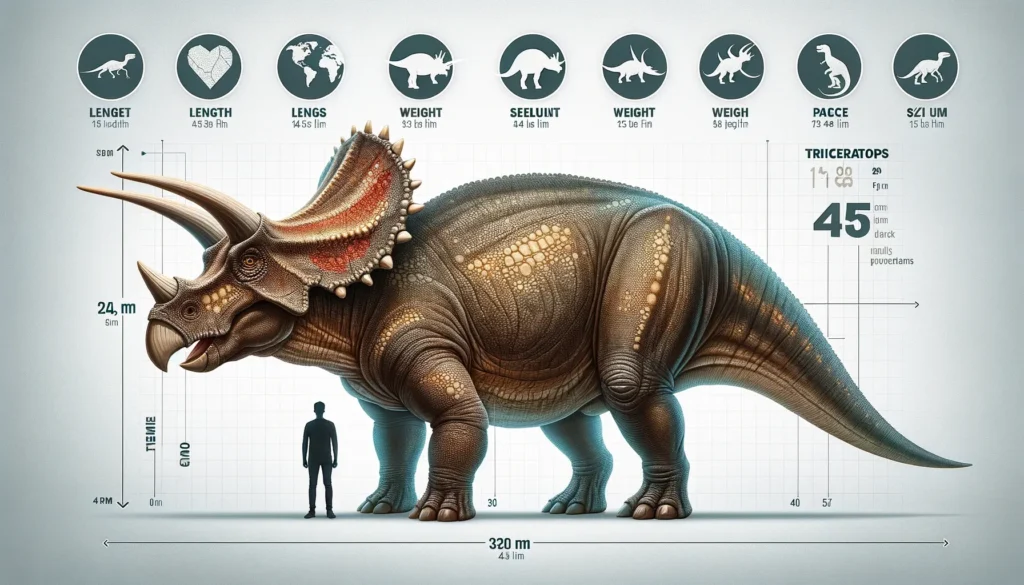
| Length | Up to 9 meters (30 feet) |
| Weight | Up to 12,000 kilograms (26,000 pounds) |
| Size | Large |
| Posture | Quadrupedal |
| Locations | USA, Canada |
| Continent | North America |
| Type | Ceratopsians |
| Habitats | Forest, Grasslands, Floodplains |
Description of Triceratops
Historical Context
Triceratops was first discovered in 1887 by John Bell Hatcher, an American paleontologist who named it “three-horned face” in Greek. Triceratops fossils have been found in the Hell Creek Formation of western North America, as well as in other formations in the USA and Canada. Triceratops was one of the last surviving dinosaurs, along with Tyrannosaurus rex, before the mass extinction event that wiped them out.
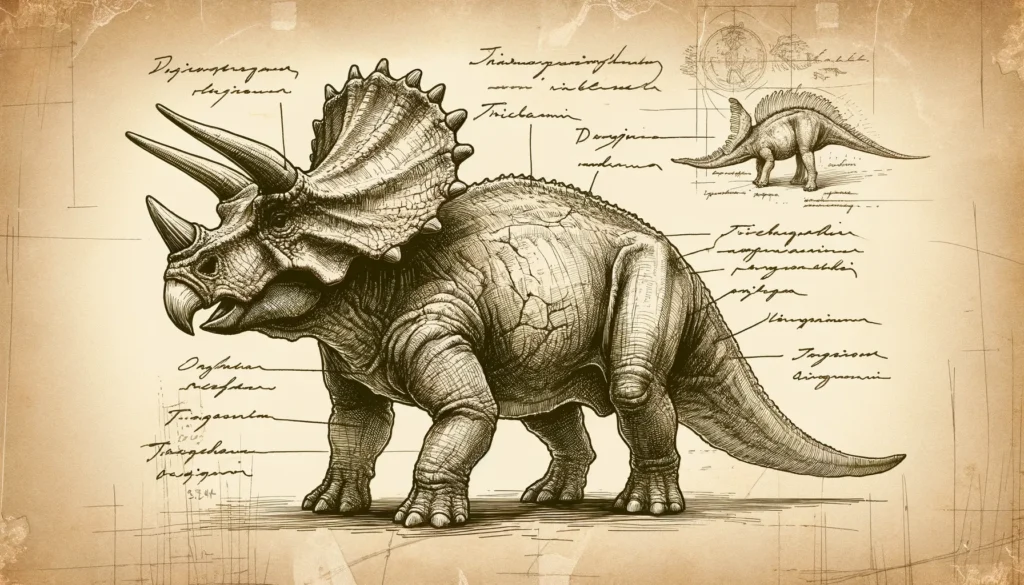
Physical Attributes
Triceratops had a large head with a beak-like mouth and shearing teeth that were adapted for cutting tough plant matter. It had three horns on its face: two long brow horns above its eyes and a shorter nasal horn on its snout. The horns were made of bone covered by keratin, the same material that makes up human nails and hair. The horns were probably used for fighting or competing with other Triceratops, as well as for defending against predators. Triceratops also had a massive frill of bone at the back of its skull, which was decorated with various bumps and spikes. The frill was probably used for display (signaling to mates or rivals) or protection (shielding the neck from attacks).
Feeding Habits
Triceratops was a herbivore that fed on low-growing plants such as ferns, cycads and palms. It had a large gut that could digest fibrous plant material. Triceratops may have swallowed stones (gastroliths) to help grind up the food in its stomach. Triceratops was not very picky about what it ate, and may have consumed some insects or small animals by accident.
Unique Features
Triceratops had one of the largest skulls relative to its body size of any land animal. Its skull could easily reach a length of over 2 meters (7 feet). The skulls of different Triceratops varied in size and shape, depending on their age, sex and species. Some paleontologists have suggested that there were two main types of Triceratops: one with a long and narrow skull and one with a short and wide skull. These types may have represented different sexes or different species.
Movement and Speed
Triceratops was a slow-moving dinosaur that walked on four legs. Its front legs were shorter than its hind legs, which gave it a hunched posture. Its feet had hoof-like claws that helped it grip the ground. Triceratops could not run very fast, but it could probably reach speeds of up to 15 kilometers per hour (10 miles per hour). Triceratops was not very agile or flexible, and had difficulty turning or changing direction quickly.
Cultural Impact
Triceratops is one of the most popular and recognizable dinosaurs in the world. It has appeared in many books, movies, TV shows, games and toys. It is often depicted as a brave or loyal creature, despite its herbivorous diet. Triceratops is also a symbol of Wyoming, where many fossils have been found. It is the state dinosaur of Wyoming and the mascot of the University of Wyoming.

Interesting Facts
- Triceratops means “three-horned face” in Greek.
- The word “ceratopsian” for the group of horned and frilled dinosaurs was derived from Triceratops.
- Triceratops lived alongside other famous dinosaurs such as Tyrannosaurus rex, Ankylosaurus and Edmontosaurus.
Related Dinosaurs
- Velociraptor: A small, feathered carnivore known for its speed and agility.
- Anchiceratops: A herbivore with three horns and a large frill, often considered the nemesis of the T-Rex.
- Brachiosaurus: A massive, long-necked herbivore that towered over most other dinosaurs.







