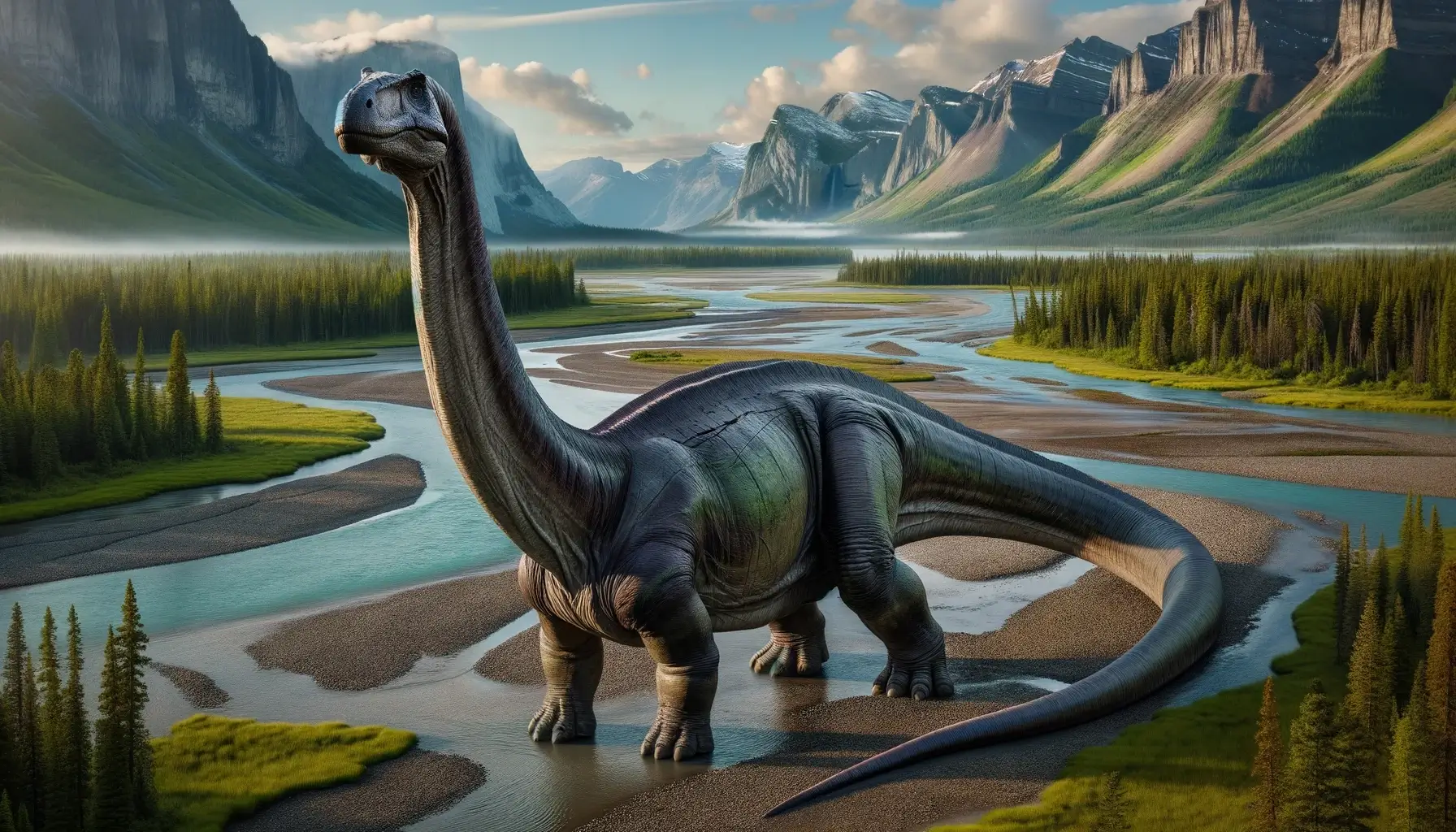
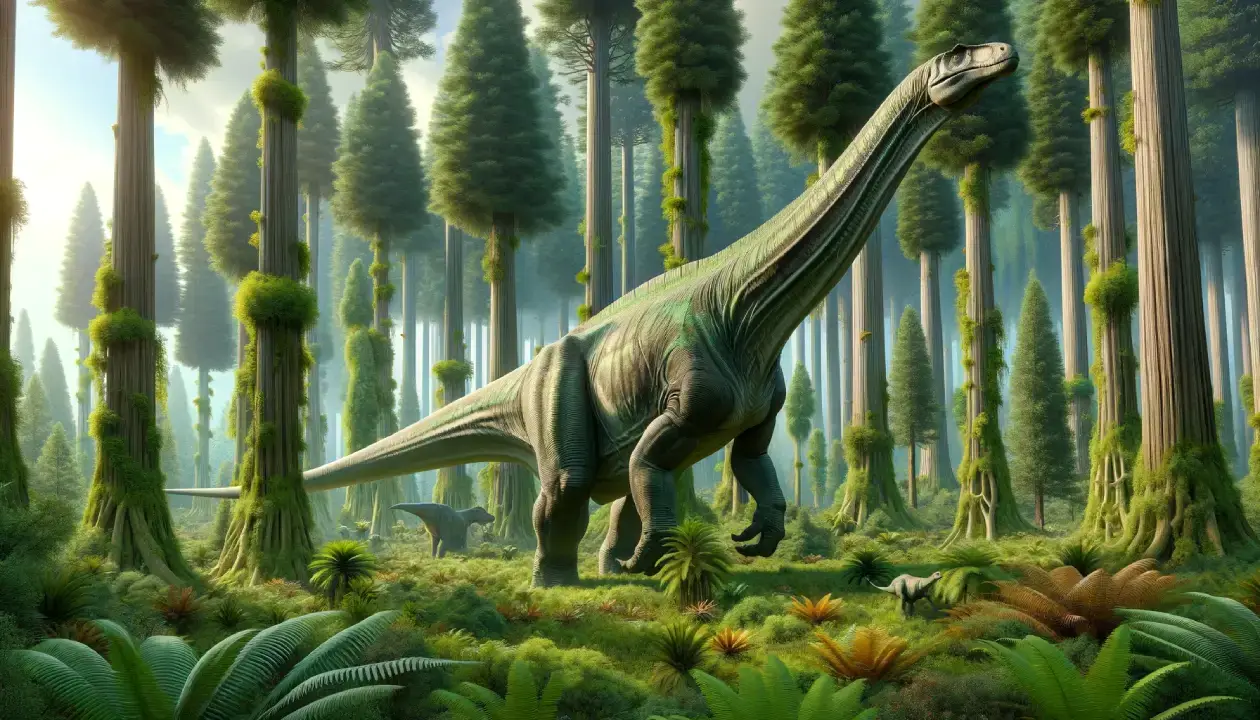
Apatosaurus was a massive sauropod dinosaur that lived in what is now North America during the Late Jurassic period, about 150 million years ago. It was one of the first dinosaurs to be discovered in the USA, and its name means “deceptive lizard”. It had a long neck and tail, but also carried armor in the form of osteoderms. These were bony plates or spikes that covered its back and neck, and may have helped it defend itself from predators. It was a herbivore that fed on low-growing plants and had a small brain relative to its body size.

Basic Information
| Feature | Details |
| Time Period | Late Jurassic (152-150 million years ago) |
| Diet | Herbivore |
| Length | 21-23 meters (69-75 feet) |
| Weight | 16.4-22.4 metric tons (18.1-24.7 short tons) |
| Size | Large |
| Posture | Quadrupedal |
| Locations | USA |
| Continent | North America |
| Type | Sauropods |
| Habitats | Forest, Grasslands, Floodplains |
Description of Apatosaurus
Historical Context
Apatosaurus was one of the first sauropod dinosaurs to be discovered and named by the famous paleontologist Othniel Charles Marsh in 1877. However, it was not the only name he gave to this dinosaur. In 1879, he named another sauropod specimen as Brontosaurus, meaning “thunder lizard”. For many years, these two names were used interchangeably for the same dinosaur, until it was realized that they were actually synonyms and that Apatosaurus had priority over Brontosaurus. However, the name Brontosaurus became more popular and widely used in books, movies, and toys, creating confusion among the public. In 2015, a new study suggested that Brontosaurus might be a valid genus after all, distinct from Apatosaurus. The debate is still ongoing among paleontologists.
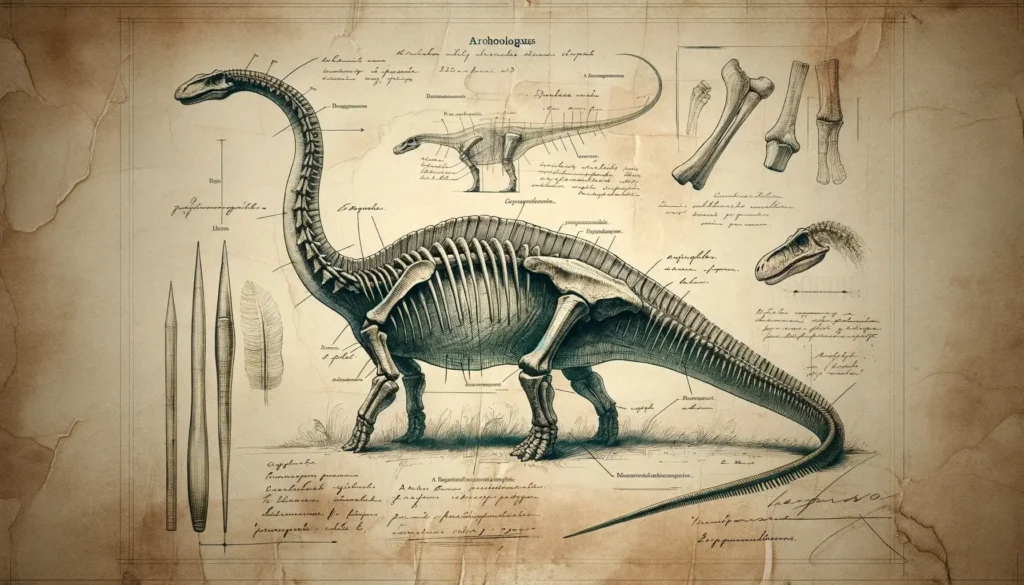
Physical Attributes
Apatosaurus was a gigantic herbivorous dinosaur that belonged to the group of sauropods, which were characterized by their long necks, long tails, and four-legged stance. Apatosaurus was a member of the subgroup of diplodocids, which were the most slender and graceful sauropods in the Late Jurassic. Apatosaurus had a broad, low-slung body with short legs and a long tail. Its head was wide and flat, with small eyes and nostrils that faced sideways rather than forward. Its jaws were covered with a horny beak and had small, peg-like teeth for cropping plants. Its most distinctive feature was its neck, which was longer than any other sauropod except for Diplodocus. The neck had fifteen vertebrae that were elongated and flexible, allowing Apatosaurus to reach high up in the trees for food.
Feeding Habits
Apatosaurus was a herbivore that fed on low-growing plants such as ferns, cycads, and horsetails. It had a broad muzzle that allowed it to take large bites of vegetation. It did not have complex teeth for chewing, so it swallowed its food whole or with minimal processing. It had a large gut that could digest tough plant matter with the help of symbiotic bacteria. Apatosaurus may have used its long neck to browse on different levels of the forest canopy, avoiding competition with other herbivores.
Unique Features
Apatosaurus had several unique features that distinguished it from other diplodocids and dinosaurs. One of them was its tail, which was very long and muscular. The tail had about eighty vertebrae that were stiffened by tendons and ligaments. The tail could be used as a whip to fend off predators or communicate with other members of the herd. Some studies have suggested that Apatosaurus could crack its tail at over 200 decibels, louder than a gunshot or a jet engine. Another unique feature was its posture, which was more horizontal than vertical. Apatosaurus held its neck and tail parallel to the ground, rather than arching them upward or downward. This posture may have helped Apatosaurus balance its massive body and reduce stress on its bones and muscles.
Movement and Speed
Apatosaurus was not a fast or agile dinosaur. It walked on four legs and had a low center of gravity, which made it stable but also limited its mobility. It could not turn quickly or run for long distances. Its top speed has been estimated to be around 17 km/h (11 mph), similar to an elephant’s pace. However, it could make sudden movements when necessary, such as raising its head or swinging its tail.
Cultural Impact
Apatosaurus has been featured in many books, movies, games, and toys as a popular dinosaur. It is often portrayed as a gentle giant or a loyal companion for human characters. Some examples of its appearances in popular culture are The Land Before Time (1988), Jurassic Park (1993), The Good Dinosaur (2015), Dinosaur Train (2009-present), and Dino Dan (2010-2013).
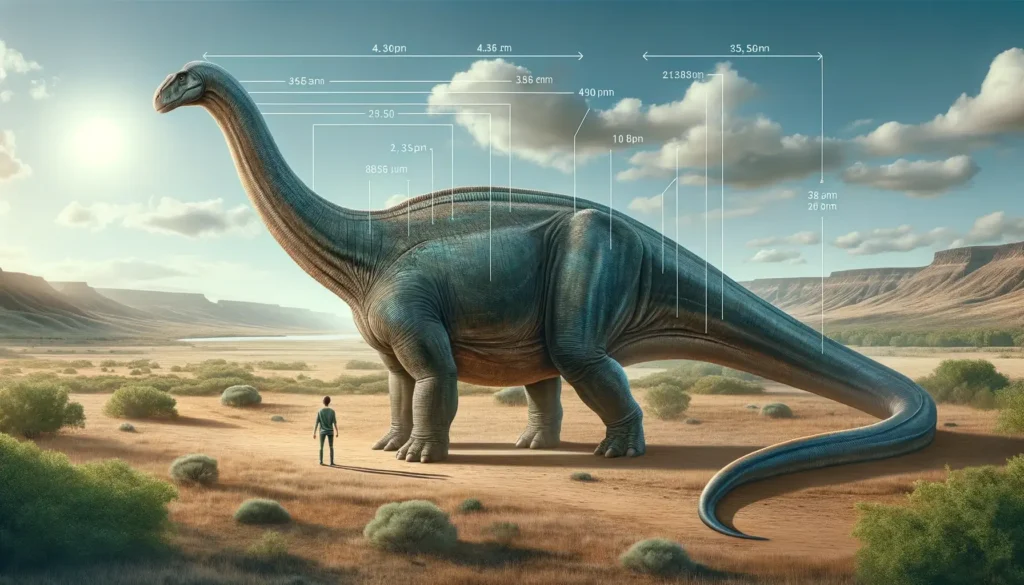
Interesting Facts
- Apatosaurus was one of the largest land animals of all time. It reached a length of 21-23 meters (69-75 feet), weighed 16.4-22.4 metric tons (18.1-24.7 short tons), and stood 4.5 meters (15 feet) tall at the hips.
- Apatosaurus lived about 152 to 150 million years ago, during the late Kimmeridgian to early Tithonian age, and are now known from fossils in the Morrison Formation of modern-day Colorado, Oklahoma, New Mexico, Wyoming, and Utah in the United States.
- Apatosaurus was originally named Brontosaurus by Othniel Charles Marsh in 1879, but this name was later synonymized with Apatosaurus by Elmer Riggs in 1903. However, in 2015, a new study suggested that Brontosaurus might be a valid genus after all, distinct from Apatosaurus.
- Apatosaurus had a very long neck that was longer than any other sauropod except for Diplodocus. The neck had fifteen vertebrae that were elongated and flexible, allowing Apatosaurus to reach high up in the trees for food.
- Apatosaurus could crack its tail at over 200 decibels, louder than a gunshot or a jet engine. The tail could be used as a whip to fend off predators or communicate with other members of the herd.
Related Dinosaurs
- Diplodocus: A close relative of Apatosaurus that had a longer neck and tail and a more slender body.
- Brachiosaurus: Another close relative of Apatosaurus that had a taller neck and a shorter tail and was one of the heaviest dinosaurs ever known.
- Barosaurus: A more distant relative of Apatosaurus that had an extremely long neck and tail and was one of the longest dinosaurs ever known.







