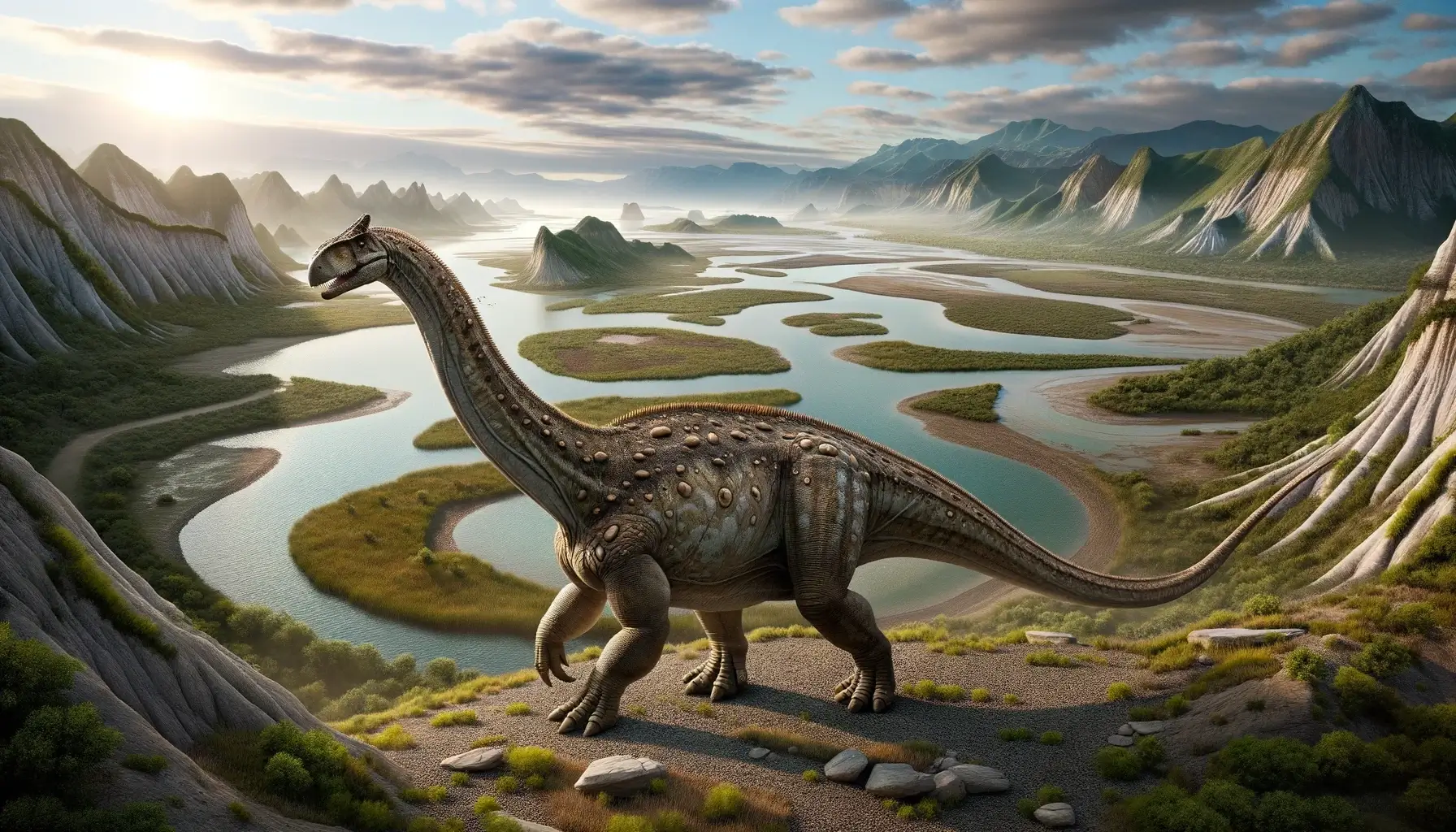
Ampelosaurus was a large plant-eating dinosaur that lived in what is now France during the Late Cretaceous period, about 70 million years ago. It was one of the first dinosaurs to be discovered in the Aude region, and its name means “vine lizard”. It had a long neck and tail, but also carried armor in the form of osteoderms. These were bony plates or spikes that covered its back and neck, and may have helped it defend itself from predators.

Basic Information
| Feature | Details |
| Time Period | Late Cretaceous, 71.5 million years ago |
| Diet | Herbivore |
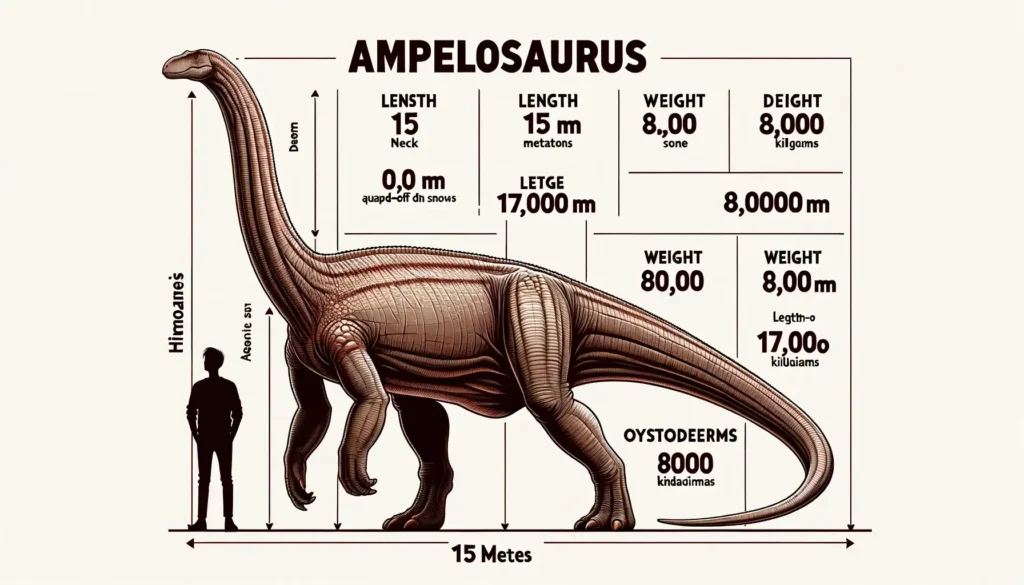
| Length | 15 m (49 ft) |
| Weight | 5 tonnes (5.5 tons) |
| Size | Large |
| Posture | Quadrupedal |
| Locations | France |
| Continent | Europe |
| Type | Sauropod |
| Habitats | Grasslands, Floodplains |
Description of Ampelosaurus
Historical Context
Ampelosaurus was one of the first sauropods to be discovered in Europe, and the oldest known from that continent. It was named by Jean Le Loeuff in 1995, based on a partial skull found in the Horseshoe Canyon Formation of Alberta, Canada. The name Ampelosaurus means “”vine lizard””, referring to the vineyards near the fossil site. Ampelosaurus is considered a titanosaur, a group of sauropods that had armor in the form of bony plates or spikes on their skin. It lived during the late Cretaceous period, about 71.5 million years ago, and shared its habitat with other dinosaurs such as Tarascosaurus, Pyroraptor, and Rhabdodon.
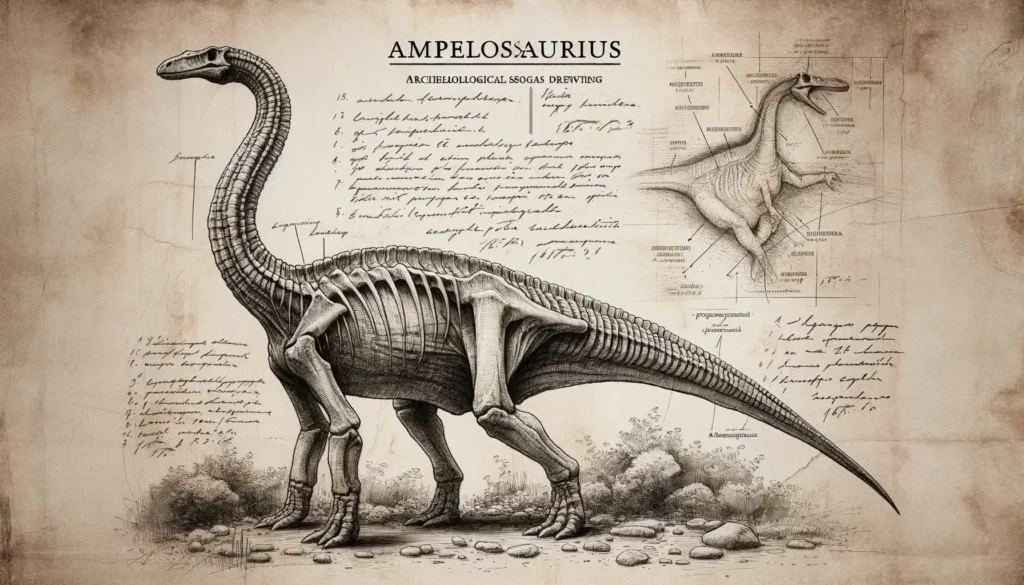
Physical Attributes
Ampelosaurus was a large, quadrupedal dinosaur with a long neck and tail. It had a robust body, supported by four stout legs with five-toed feet. Its head was relatively small, with a short snout and nostrils placed high on the skull. Its teeth were peg-like, adapted for cropping plants. Ampelosaurus had armor on its back, neck, and tail, consisting of bony plates (osteoderms) that varied in size and shape. Some of the osteoderms were spiky, while others were flat or round. The function of the armor is not clear, but it may have provided protection from predators or helped with thermoregulation.
Feeding Habits
Ampelosaurus was an herbivore, feeding on low-growing plants such as ferns, cycads, and conifers. It used its long neck to reach vegetation that was out of reach for other dinosaurs. It may have also used its tail as a counterbalance when rearing up on its hind legs to access taller plants. Ampelosaurus had a simple digestive system, relying on bacterial fermentation to break down plant fibers. It may have swallowed stones (gastroliths) to help grind up the food in its stomach.
Unique Features
Ampelosaurus had several features that distinguished it from other sauropods. One of them was its armor, which was more extensive and diverse than that of most other titanosaurs. The armor may have been used for defense against predators or for display to attract mates or intimidate rivals. Another unique feature of Ampelosaurus was its growth rate, which was slower than that of other sauropods. This may have been related to its island environment, where resources were limited and competition was high.
Movement and Speed
Ampelosaurus was a slow-moving dinosaur, due to its large size and heavy body. It walked on four legs, using a columnar stance with straight limbs and upright feet. It may have been able to run at short bursts of speed, but not for long distances or sustained periods. It probably relied on its size and armor to deter predators, rather than agility or speed.
Cultural Impact
Ampelosaurus is not a very well-known dinosaur among the general public, as it has not been featured in many popular media or cultural works. However, it is an important dinosaur for paleontologists and scientists, as it provides valuable information about the evolution and diversity of titanosaurs in Europe. Ampelosaurus is also significant for being one of the few dinosaurs that lived on an island in the Late Cretaceous, showing how dinosaurs adapted to different environments.
Interesting Facts
- Ampelosaurus was named after the vineyards near the fossil site, but it also had another meaning: ampelos is a Greek word for “”vine””, which was also the name of a satyr who was turned into a grapevine by Dionysus.
- Ampelosaurus lived on what was the Ibero-Armorican Island, a landmass that included much of present-day France and Spain. This island was isolated from other continents by rising sea levels during the Late Cretaceous.
- Ampelosaurus may have been related to another titanosaur from South America: Saltasaurus, which also had armor on its skin.
Related Dinosaurs
- Saltasaurus: A titanosaur from Argentina that lived in the Late Cretaceous, about 70 million years ago.
- Lirainosaurus: A titanosaur from Spain that lived in the Late Cretaceous, about 66 million years ago.
- Magyarosaurus: A titanosaur from Romania that lived in the Late Cretaceous, about 70 million years ago.







